How to Synchronize Files and Directories Using Rsync
Overview
Rsync is an open source utility for efficiently transferring and synchronizing files from one host to an another host. This tool is powerful because it can be a server and client. Rsync usually used to automate backup data from server to backup server.
The advantages of using rsync:
Save Bandwidth and Supports Resume
Flexibel
Fast
Easy Setup
Some Basic Options of Rsync Command:
| Options | Function |
|---|---|
| -v, --verbose | increase verbosity |
| -a, --archive | archive mode |
| -r, --recursive | recurse into directories |
| -u, --update | skip files that are newer on the receiver |
| -e, --rsh=COMMAND | specify the remote shell to use |
| -z, --compress | compress file data during the transfer |
| -h, --human-readable | output numbers in a human-readable format |
let's go ahead and follow the tutorial to gain experience on Rsync.
Prerequisites
This is the prerequisites before you start the tutorial.
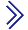
- Create two host in local environment or you can use VPSServer.com[1]
In this tutorial used VPSServer.com[2] service to create two host using Ubuntu OS but you can also using this tutorial for other distro such as CentOS, Fedora, Debian, etc.
Install Rsync
Rsync installation is very easy just by following the command
for Debian / Ubuntu
root@host-ubuntu:~# apt-get install rsync
for Fedora / CentOS / Scientific
root@host-centos:~# yum install rsync
That's it. Now you have rsync in your server :)
Synchronize Files / Directories on Local Server
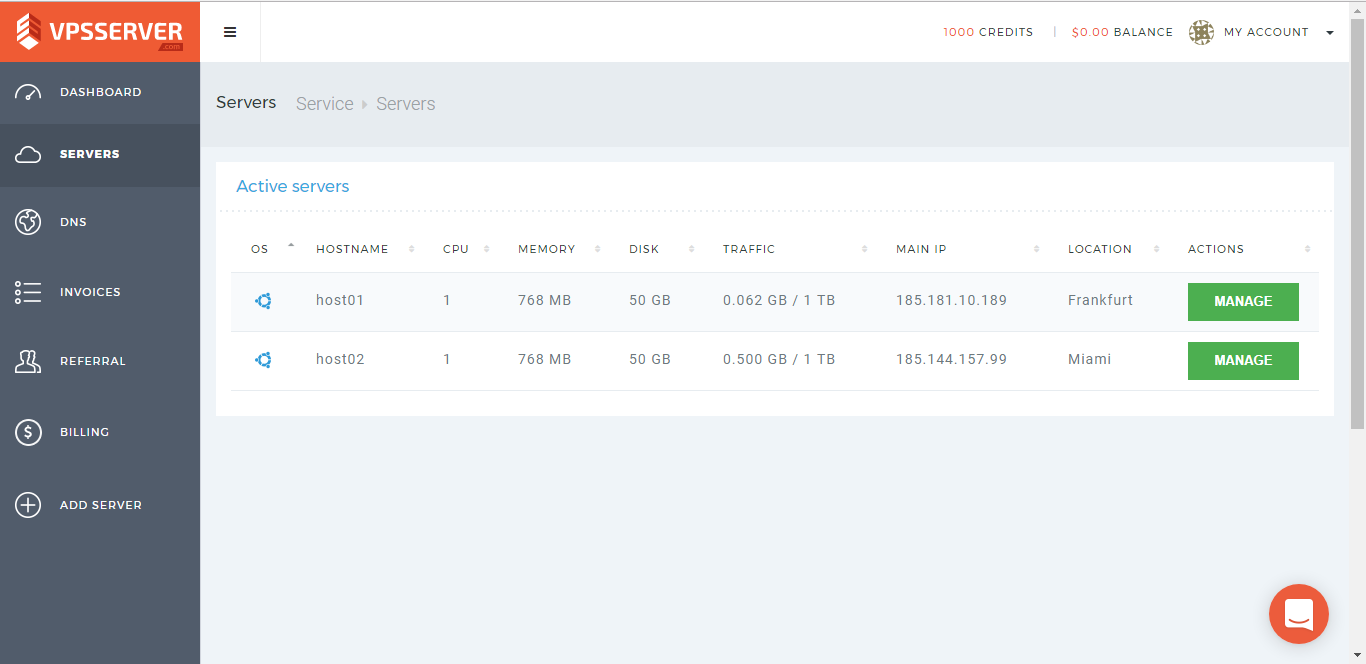
- create folder "primary" and files (file1, file2, file3) on the primary folder.
root@host01:~# mkdir primary
root@host01:~# touch primary/file{1..3}
check the folder and files, then fill the files with text
root@host01:~# ls primary/ root@host01:~# echo "im in file1" > primary/file1 && echo "im in file2" > primary/file2 && echo "im in file3" > primary/file3 root@host01:~# cat primary/file1 root@host01:~# cat primary/file2 root@host01:~# cat primary/file3
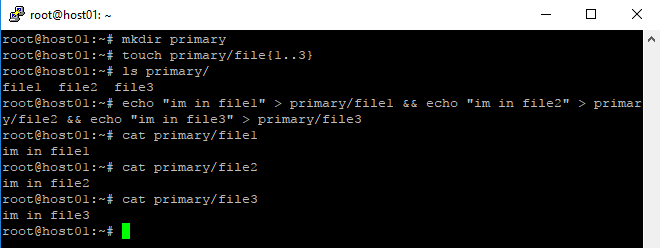
- Sync the primary folder from /root/primary/ to /tmp/secondary/
root@host01:~# rsync -avzh primary/ /tmp/secondary
Check the synchronize files
root@host01:~# ls /tmp/secondary/ root@host01:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file1 root@host01:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file2 root@host01:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file3
Synchronize Files / Directories from Local Server to a Remote Server
- Sync the primary folder in host01 to secondary folder in host02
root@host01:~# rsync -avz primary/ root@185.144.157.99:/tmp/secondary/
Check the synchronize files
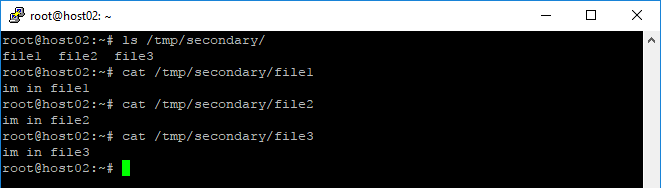
root@host02:~# ls /tmp/secondary/ root@host02:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file1 root@host02:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file2 root@host02:~# cat /tmp/secondary/file3
Synchronize Files / Directories from a Remote Server to a Local Server over SSH
- Sync the secondary folder in host02 to primary folder in host01
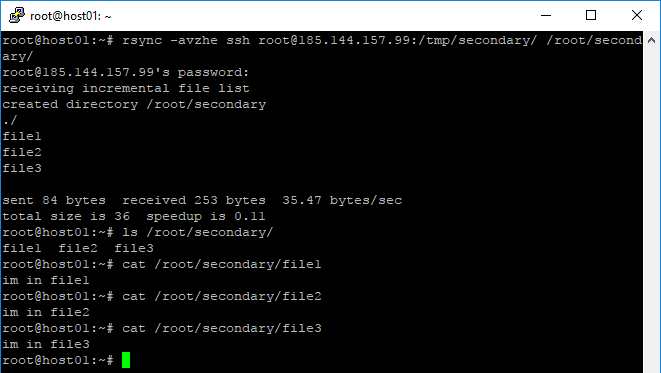
root@host01:~# rsync -avzhe ssh root@185.144.157.99:/tmp/secondary/ /root/secondary/
Check the synchronize files
root@host01:~# ls /root/secondary/ root@host01:~# cat /root/secondary/file1 root@host01:~# cat /root/secondary/file2 root@host01:~# cat /root/secondary/file3
Synchronize Files / Directories from a Local Server to a Remote Server over SSH
- Sync the primary folder in host01 to secondary folder in host02 via SSH
root@host01:~# rsync -avzhe ssh primary/ root@185.144.157.99:/home/secondary
Check the synchronize files
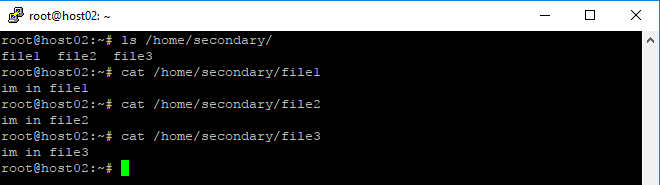
root@host02:~# ls /home/secondary/ root@host02:~# cat /home/secondary/file1 root@host02:~# cat /home/secondary/file2 root@host02:~# cat /home/secondary/file3
Show Progress While Synchronize Files / Directories
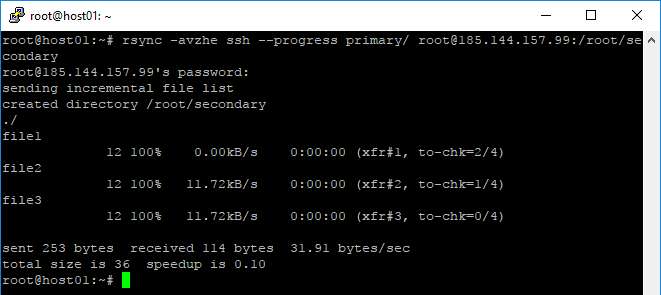
- You can use --progress to show progress while synchronize files / directories from host01 to host02
root@host01:~# rsync -avzhe ssh --progress primary/ root@185.144.157.99:/root/secondary
Set Bandwidth Limit
- You can also set --bwlimit parameter with a kbps value while synchronize files / directories
root@host01:~# rsync --bwlimit=100 -avzhe ssh primary/ root@185.144.157.99:/opt/secondary
That's it. Installation and basic operation of Rsync. I hope you can understand rsync from this tutorial. If you encounter any bugs or documentation errors, please comments below :)
[1]: https://www.vpsserver.com/
[2]: https://www.vpsserver.com/